Hello folks! Welcome to my blog on Terraform. I'm Chris Jonathan. I write blogs on DevOps content.
To see all my blogs on DevOps, Click here.
Let's dive into today's blog 💪
Overview of Terraform
Let's understand what is terraform
Terraform allows you to automate and manage your infrastructure, your platform and services that run on that platform.
It's open source and uses declarative language.
Use-Cases - Terraform
It's a tool for:
Infrastructure Provisioning:
Suppose you create an application and you need to set up an infrastructure where you can run that application. And this requires certain steps which include:
Creating a VPC, Spinning up the servers, creating AWS users and permissions, installing Docker and many other steps according to the necessity of the project. And terraform does all these with ease and that too in a correct order.
Managing Existing Provision:
Once you created your initial infrastructure for your project, you will be continually adjusting and changing it and because of that, you will need an automation tool that will do most of the heavy lifting for you so that you don’t have to manually figure and some stuff. And that's Terraform
Replicating Infrastructure:
You can easily spin up an identical infrastructure and set it up using the terraform code that you use for the main setup.
Terraform automates this process.
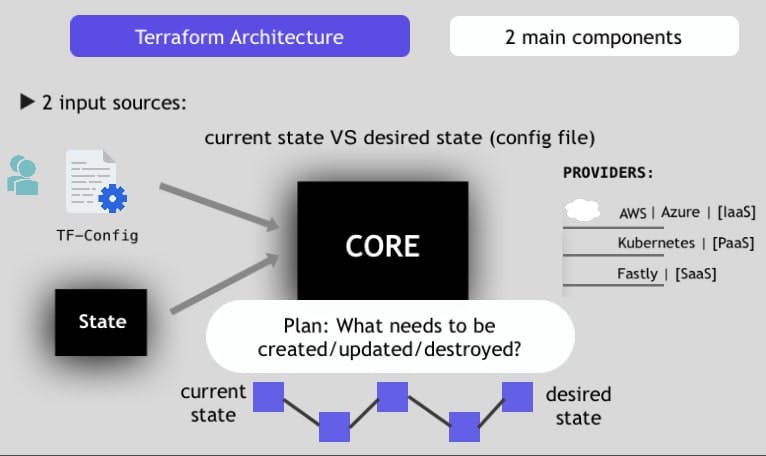
Architecture - Terraform
How does terraform work?
It has two main components:
CORE:
It has 2 input sources:
-> TF-Config file: Where the user writes and configures the code.
-> TF-State: Where terraform keeps the UpToDate state of how the current setup of the infrastructure looks like.
So, the core takes its inputs and figures out the plan of what needs to be done.
PROVIDERS:
Terraform can work with over 100 providers
Some of the providers:
AWS | Azure | [IaaS]
Kubernetes | [PaaS]
Fastly [SaaS]
For example, it creates a VPC, launches an EC2 instance on AWS and many more.
Hands-on - Terraform
Now let's open VS-Code and see what we can do with Terraform config file
Note: Firstly, we must learn to use the Documentation of Terraform without which we can’t use terraform because we don’t know the script format for different cloud providers
For this blog let us assume we are working on the AWS provider.
This is the terraform documentation of the AWS provider.
.Tf file
Now create the .tf file which is the extension of terraform.
And add the basic contents of the AWS provider which is available in the documentation
provider "aws" {
region = "us-west-1"
access_key = "my-access-key"
secret_key = "my-secret-key"
}
"access_key" and "secret_key" are the security keys of your AWS account
Launch an EC2 instance
To launch an Ubuntu-based EC2 instance on AWS👇
resource "aws_instance" "demoserver" {
ami = "ami-id"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
tags = {
Name = "ubuntu"
}
"ami" and "instance_type" are your instance's ID and type.
"demoserver" is the name of the server
Create a VPC
To create a VPC on AWS👇
resource "aws_vpc" "main" {
cidr_block = "10.0.0.0/16"
instance_tenancy = "default"
tags = {
Name = "main"
}
}
Terminal Commands - Terraform
After writing the script, we need to run some commands to get it working on the cloud provider.
So open the terminal and change the directory to the current working directory.
Commands:
terraform init - downloads the necessary plugins to interact with the provider
terraform plan - creates an execution plan, which lets you preview the changes that terraform plans to make to your infrastructure
terraform apply - runs our code and we can see the changes made in the provider's console
terraform apply -target (resource name) - will deploy only the specific resource that is mentioned
terraform apply --auto-approve - same as the above but will skip the verification part by auto approving
terraform refresh - will display all the changes without deploying
terraform destroy - deletes all the instances(instances in the file) from the console
terraform destroy -target (resource name) - will destroy only the specific resource that is mentioned
terraform state list - shows all the resources we have used
terraform state show (resource name) - displays all the information about that resource
To delete a specific instance:
Delete the specific resource in the code and then run terraform apply and the specific instance will be deleted
Conclusion
That's it for the blog guys. I hope you found this blog helpful.
I've learned Terraform from freeCodeCamp.org's Terraform Course
To know about me:
Twitter: twitter.com/Chris__Jonathan
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/chris-jonathan
Thanks, guys 😊
